Exploring the Essential Elements of ANSYS: A Comprehensive Guide
In Finite Element Analysis (FEA), there are various types of elements used to represent different physical phenomena and geometries. Here are some commonly used element types and their practical applications:
1D Elements:
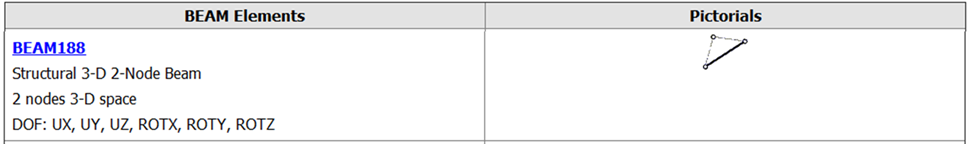
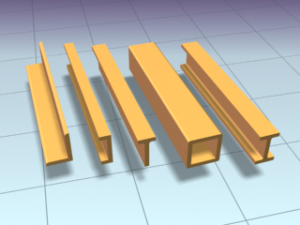
Beam Element: Represents a linear structural member with a length but negligible thickness in comparison, allowing for the analysis of bending, axial, and shear behavior. It is often used for analyzing beam structures, such as bridges or building frames. The beam element is typically represented as a line segment.
Truss Element: Represents a one-dimensional member with no bending stiffness, making them useful for analyzing structures primarily subjected to axial forces. It is commonly used for analyzing truss structures or skeletal frameworks. The truss element is represented as a line segment with nodes at each end.
2D Elements:
Triangle Element: Represents a two-dimensional element with three nodes forming a triangular shape. It is frequently used in plane stress or plane strain analysis. Triangle elements are effective for modeling irregular geometries and are particularly useful for analyzing thin structures subject to in-plane loads. The triangle element is defined by three points in a two-dimensional space.
Quadrilateral Element: Represents a two-dimensional element with four nodes forming a quadrilateral shape. It is versatile and widely used in analyzing structures with complex geometries, including planar and curved surfaces. Quadrilateral elements provide flexibility in capturing various load conditions and are commonly used in general-purpose structural analysis. The quadrilateral element is defined by four points in a two-dimensional space.
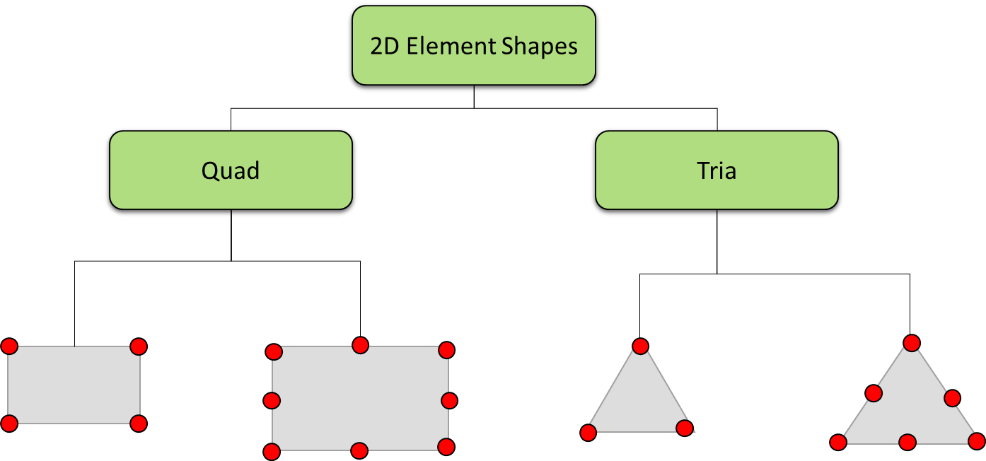
2D elements types:
- Plane stress – Stress in z direction (thickness) is 0.
- Plane strain – Strain in z direction (thickness) is 0
- Plane stress with thickness – Stress in z direction (thickness) is ≠ 0
- Axisymmetric – Stress in z direction (thickness) is 0 (in rotational direction)
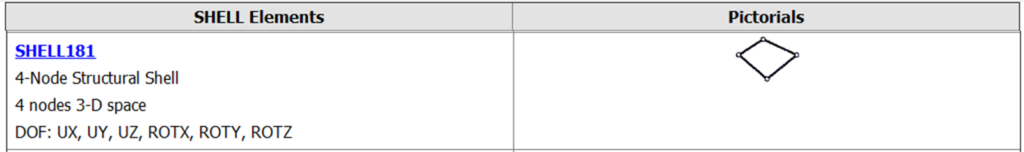
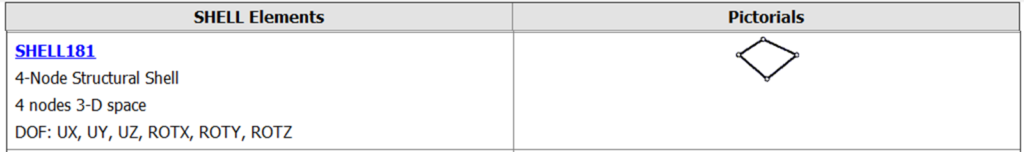
Shell Elements: Used to model thin structures, such as plates and shells. Shell elements have both in-plane and out-of-plane capabilities, allowing for the analysis of bending, membrane, and shear behavior. They are commonly employed in the analysis of structures like aerospace panels, automotive body components, and pressure vessels.
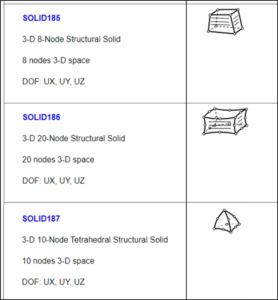
Used for modeling three-dimensional objects with volumetric properties. Solid elements provide accurate representation of internal stresses and deformations in solid materials, making them suitable for analyzing components like machine parts, mechanical assemblies, and structural components.
3D Elements:
Tetrahedron Element: Represents a three-dimensional element with four nodes forming a pyramid-like shape. It is often used for modeling irregular geometries and solid structures. The tetrahedron element is defined by ten points in a three-dimensional space. Tetrahedron elements are commonly used in applications such as fluid flow analysis, stress analysis of complex parts, and simulating deformation in biological tissues.
Hexahedron Element: Represents a three-dimensional element with eight nodes forming a cube-like shape. It is commonly used for modeling regular geometries and solid structures including blocks, beams, and plates. Hexahedron elements offer greater accuracy and efficiency for certain types of analyses, such as thermal analysis or static stress analysis of solid objects.
Pyramid Element: Represents a three-dimensional element with twenty nodes forming a cube/tet/pyramid like shape. It is often used for modeling irregular geometries and solid structures. It is of second order element with mid-side nodes. Pyramid elements are widely used for capturing critical locations at regular geometry and to connect hexahedron and tetrahedron element.
The choice of element type in FEA depends on various factors such as the specific application, geometry, and desired level of accuracy. FEA software packages like ANSYS offer a range of element options to accommodate different engineering problems and ensure efficient and accurate analysis of structures and systems.
If you are interested in enrolling in an ANSYS course in India, I recommend searching online for educational institutions which was curated by IIT and experienced faculty in Hyderabad i.e., from Artem Academy. You can explore various options, compare their course content, duration, and instructor expertise to find the one that best suits your needs.