GD&T: A Beginner’s Guide to Precision Engineering
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is a vital language in the realm of engineering and manufacturing, serving as a set of symbols and principles that convey precise specifications for the design and production of mechanical components. GD&T plays a crucial role in enhancing communication between designers, engineers, and manufacturers, ensuring that everyone involved in the process interprets design intent accurately.
Understanding the Basics of GD&T
At its core, GD&T is a symbolic language that allows designers to communicate geometric characteristics and tolerances more precisely than traditional methods. Unlike traditional dimensioning, which primarily focuses on size, GD&T incorporates symbols and annotations to convey information about form, orientation, location, and runout.
The fundamental elements of GD&T include:
-
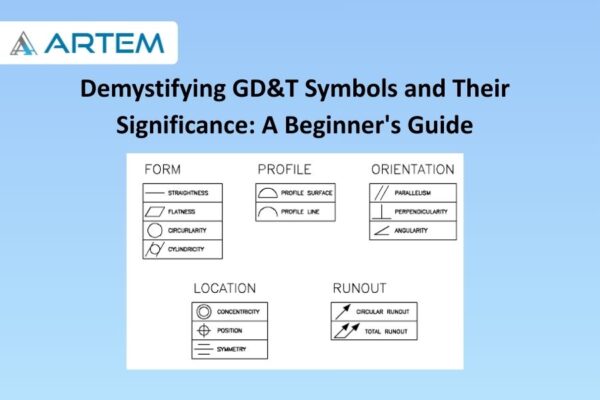
- Symbols: GD&T uses a set of symbols to represent various geometric characteristics and tolerances. Common symbols include position, concentricity, perpendicularity, and parallelism.
- Datums: Datums are reference points or planes that serve as the basis for measurements and tolerances. They establish the coordinate system for the part.
- Feature Control Frames: These frames encapsulate the GD&T symbols and provide a compact way to communicate the desired tolerances and geometric characteristics for a specific feature.
Importance of GD&T in Engineering Drawings
GD&T is essential for several reasons:
-
- Precision and Clarity: GD&T provides a clear and precise way to communicate design requirements. This minimizes ambiguity and reduces the likelihood of misinterpretation.
- Uniformity: Standardizing on GD&T promotes consistency across design and manufacturing processes, ensuring that everyone in the supply chain understands and adheres to the specified tolerances.
- Cost Reduction: By accurately defining tolerances, GD&T helps optimize manufacturing processes, reducing the likelihood of defects and rework. This, in turn, lowers production costs.
- Global Compatibility: GD&T is an internationally recognized standard, making it easier for companies to collaborate on a global scale. Engineers and manufacturers worldwide can understand and implement GD&T specifications.
Getting Started with GD&T
For beginners, delving into GD&T can be a bit overwhelming. However, a solid foundation begins with understanding the basic symbols and concepts. Here are a few key points to kickstart your GD&T journey:
-
- Learn the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with symbols such as position, concentricity, perpendicularity, and parallelism. Each symbol conveys specific information about the geometric characteristics of a feature.
- Understand Datums: Grasp the concept of datums and their role in establishing a reference coordinate system. Datums are crucial for interpreting the tolerances specified in a drawing.
- Explore Feature Control Frames: Practice reading and creating feature control frames. These frames encapsulate the GD&T symbols, making it easier to convey design requirements for individual features.
- Take Advantage of Resources: Numerous resources, including textbooks, online courses, and software tutorials, are available to help you learn GD&T. Leverage these tools to enhance your understanding and practical application of GD&T principles.
In conclusion, GD&T is a powerful tool that elevates the precision and clarity of engineering drawings. Embracing GD&T principles not only enhances communication but also contributes to cost-effective and efficient manufacturing processes. As you embark on your GD&T journey, remember that practice and continuous learning are key to mastering this language of precision in engineering.